For example, a multi-product company can measure profitability of each product by preparing a product viz 6 benefits of mobile apps for small businesses and decide which product to continue and which one to drop. Companies are not required to present such statements to any external party, so there is no need to follow GAAP or IAS. The basic difference between a traditional income statement and a contribution margin income statement lies in the treatment of variable and fixed expenses for a period. The difference in treatment of these two types of costs affects the format and uses of two statements. You can’t directly calculate the contribution margin from the EBIT figure, without a breakdown of the fixed and variable costs for each product or service.
Break-Even Point in Dollars or Units
The gross sales revenue refers to the total amount your business realizes from the sale of goods or services. That is it does not include any deductions like sales return and allowances. Direct Costs are the costs that can be directly identified or allocated to your products. For instance, direct material cost and direct labor cost are the costs that can be directly allocated with producing your goods.
( .The difference of format:
Direct materials are often typical variable costs, because you normally use more direct materials when you produce more items. In our example, if the students sold 100 shirts, assuming an individual variable cost per shirt of $10, the total variable costs would be $1,000 (100 × $10). If they sold 250 shirts, again assuming an individual variable cost per shirt of $10, then the total variable costs would $2,500 (250 × $10). It is primarily used for external financial reporting, providing a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial performance.
Exploring Contribution Margins
As a business owner, you need to understand certain fundamental financial ratios to manage your business efficiently. These core financial ratios include accounts receivable turnover ratio, debts to assets ratio, gross margin ratio, etc. You’ll notice that the above statement doesn’t include the contribution margin.
How to determine the contribution margin
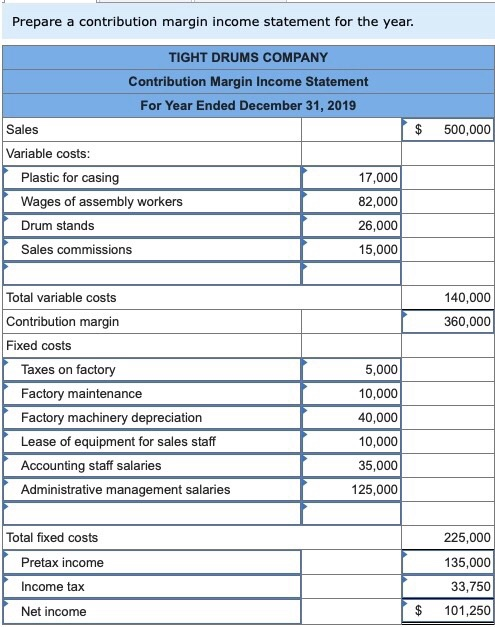
From contribution margin figure all fixed expenses are subtracted to obtain net operating income. The following simple formats of two income statements can better explain this difference. Conversely, a lower contribution margin ratio may indicate a significant portion of sales revenue is consumed by variable costs, leaving less to cover fixed costs and contribute to profit. This could prompt businesses to reassess their cost structure, pricing strategies, or operational efficiency to improve profitability.
- The contribution margin represents the amount of revenue left over after subtracting variable costs from total revenue.
- As you can see, the net profit has increased from $1.50 to $6.50 when the packets sold increased from 1000 to 2000.
- In addition, although fixed costs are riskier because they exist regardless of the sales level, once those fixed costs are met, profits grow.
- Either way, this number will be reported at the top of the income statement.
This makes the EBITDA figure important for investors looking to put money into a business. A contribution margin is a narrow view of a product or service’s profitability, but the net profit is a much wider and more comprehensive look at a company’s financial performance. Variable costs (or expenses) are any costs that do not remain consistent. These could include energy, wages (for labor related to production) or any other cost that raise or lower with the output levels of your business.
Unlike a traditional income statement, the expenses are bifurcated based on how the cost behaves. Variable cost includes direct material, direct labor, variable overheads, and fixed overheads. It does not matter if your expenses are production or selling and administrative expenses. The same thing goes with fixed expenses; they must be included in fixed costs if they are fixed. For every $1.00 of sales, a little over $.45 remains after variable costs are covered to apply toward paying fixed costs and yielding profit. The contribution margin is $145,400, and the contribution margin ratio is 45.4% ($145,400 / $320,000).
The contribution margin can help company management select from among several possible products that compete to use the same set of manufacturing resources. Say that a company has a pen-manufacturing machine that is capable of producing both ink pens and ball-point pens, and management must make a choice to produce only one of them. The contribution margin ratio of 45.4% for the company as a whole is determined as follows. As an example, a company manufactures two products and sells them in two regions, East and West, to two customers that have a presence in both regions.
The electricity expenses of using ovens for baking a packet of bread turns out to be $1. The financial data used to create these have a lot of crossovers, but they look at different aspects of a business. For instance, in Year 0, we use the following formula to arrive at a contribution margin of $60.00 per unit. The 60% CM ratio implies the contribution margin for each dollar of revenue generated is $0.60. Tickmark, Inc. and its affiliates do not provide legal, tax or accounting advice.
On the other hand, the net profit per unit may increase/decrease non-linearly with the number of units sold as it includes the fixed costs. Fixed costs are costs that are incurred independent of how much is sold or produced. Buying items such as machinery is a typical example of a fixed cost, specifically a one-time fixed cost. Regardless of how much it is used and how many units are sold, its cost remains the same.
Fixed costs are costs that may change over time, but they are not related to the output levels. These costs include equipment rent, building rent, storage space, or salaries (not related directly to production. If they are, you count them as variable costs). The contribution margin represents the revenue that a company gains by selling each additional unit of a product or good. This is one of several metrics that companies and investors use to make data-driven decisions about their business.



